Vitamin B6
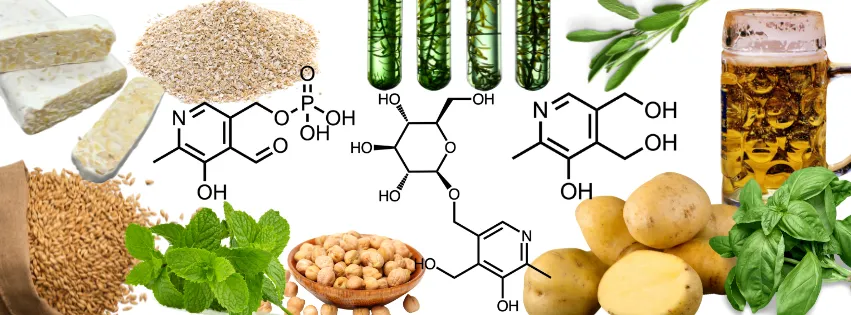
Vitamin B6 is a group of 6 vitamins from the pyridoxine group that play an essential role in human metabolism and are therefore of great importance for general health. In its active form, vitamin B6 acts as a co-enzyme in more than 150 enzymatic reactions, mainly in amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism. The conversion of amino acids into the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine is an example of a B6-catalyzed metabolic pathway, which influences mood, sleep and cognitive functions. In addition, vitamin B6 is involved in the formation of hemoglobin and supports the immune system in the synthesis of antibodies.
Like all vitamins, B6 is essential and must be supplied in sufficient quantities through food. Cereals, nuts, seeds and fish are suitable for covering the daily requirement of 1.4-1.6 mg. Our research focus in the field of B6 is on investigating the distribution of vitamins, i.e. the form in which the compound is present in food. It has been known since the 1980s that plant-based products mainly contain B6 bound to sugar, which is less easily absorbed by humans. With our new LC-MS/MS method, it is possible to detect various B6 glycosides and track their conversion during processing (e.g. during beer brewing). This allows a better assessment of the available B6.
Our publications include:
The synthesis of isotopically labelled standards for B6 vitamers
Synthetic strategies for the glykosylation of pyrixodine
The stable isotope dilution analysis of B6 vitamers in fruits, vegetables and cereals